Projects Machine learning
Dictionary learning for sound speed profiles
Dictionary learning (DL), an unsupervised machine learning method, is used to sparsely represent sound speed profiles (SSPs). In addition, DL is employed for supervised classification of SSPs.
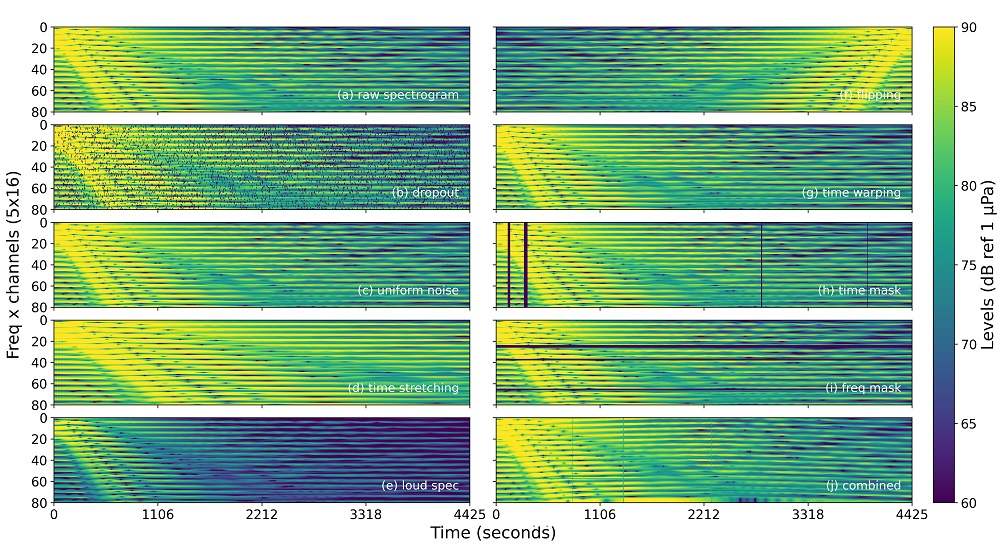
Impact of data augmentation in broadband spectrograms
Different data augmentation are applied during the training of deep learning models. Predictions for source localization and seabed classification are evaluated to assess the effectiveness of data augmentation for improving generalization of neural networks using broadband spectrograms.
Seabed classification and source localization
Deep learning algorithms such as convolutional neural networks (CNN) and residual networks (ResNet) are applied to broadband spectrograms to perform source localization and seabed classification in shallow water.

Detection of marine mammals in the Arctic
A detection and classification system (DCS) based on deep learning techniques is proposed to detect bearded seals observed during the Canada Basin Acoustic Propagation Experiment. The proposed technique reduces the laborious task of manual inspection prone to inconstant bias and possible errors in detections.

Detection and classification of fish sounds
Deep learning algorithms are implemented for detection and classification of fish sounds spotted on the east coast of the United States. The algorithms focus on the use of acoustic systems for passive acoustic monitoring of ocean vitality for fish populations. (work in progress)